WATCH
Dr. Jesudian discuss some of the AASLD Guidelines for managing OHE
SEE MORE FROM YOUR PEERS



*Comparison of Kaplan-Meier estimates of event-free curves showed XIFAXAN significantly reduced the risk of HE breakthrough by 58% during the 6-month treatment period.1
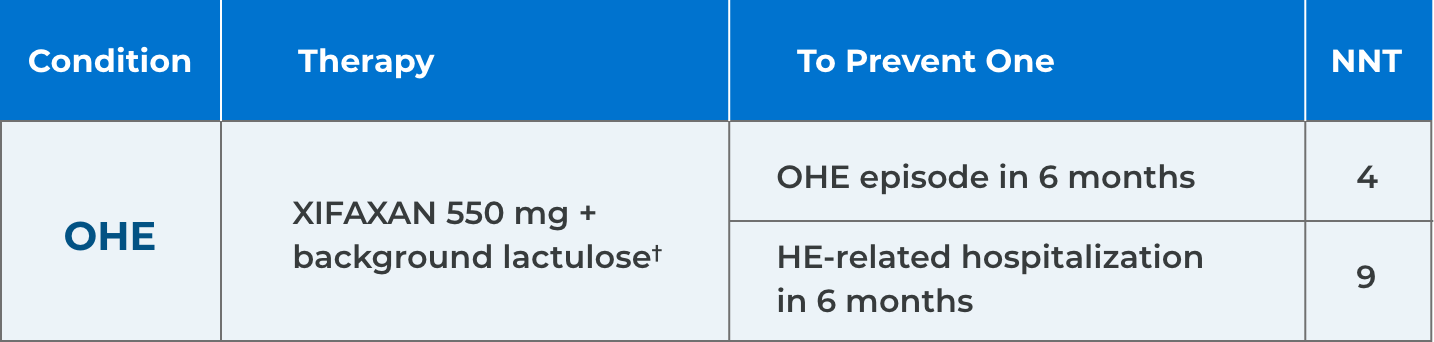
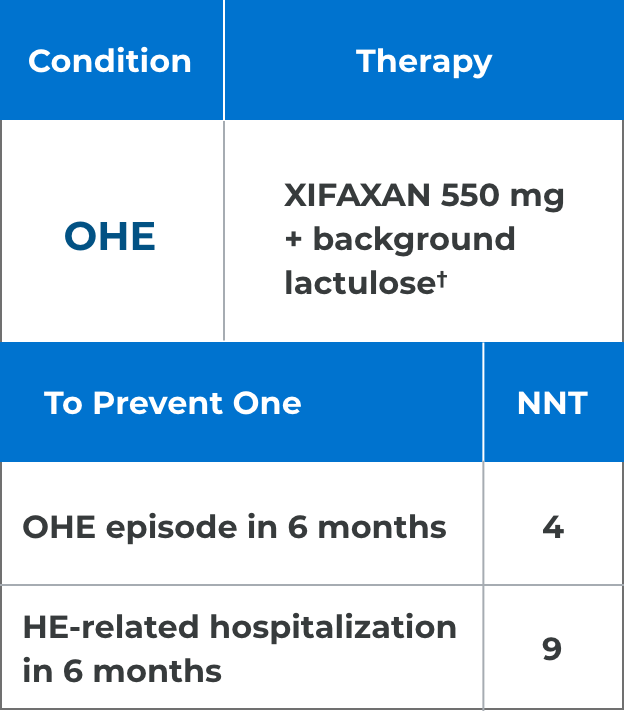
†91% of patients in the XIFAXAN group were on concomitant lactulose.1
SEE XIFAXAN SAFETY PROFILE
You should consider XIFAXAN as an add-on to lactulose for this patient.

You should consider XIFAXAN as an add-on to lactulose for this patient.

You should consider prescribing XIFAXAN in addition to lactulose.

You should consider XIFAXAN for this patient.

You might consider XIFAXAN for this patient.

‡Per the GRADE System for Evidence: Grade I=randomized, controlled trials; A=evidence is “high quality,” and further research is very unlikely to change our confidence in the estimated effect; and 1=recommendation is “strong,” with factors influencing strength of recommendation including the quality of evidence, presumed patient-important outcomes, and costs.3
AASLD, American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases; EASL, European Association for the Study of the Liver; HE, hepatic encephalopathy; OHE, overt hepatic encephalopathy; PCP, primary care physician.
References: 1. XIFAXAN. Prescribing information. Salix Pharmaceuticals; 2023. Accessed November 20, 2024. https://shared.salix.com/globalassets/pi/xifaxan550-pi.pdf 2. Bass NM, Mullen KD, Sanyal A, et al. Rifaximin treatment in hepatic encephalopathy. N Engl J Med. 2010;362(12):1071-1081. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0907893 3. Vilstrup H, Amodio P, Bajaj J, et al. Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: 2014 practice guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the European Association for the Study of the Liver. Hepatology. 2014;60(2):715-735. doi:10.1002/hep.27210
XIFAXAN® (rifaximin) 550 mg tablets are indicated for the reduction in risk of overt hepatic encephalopathy (HE) recurrence in adults and for the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea (IBS-D) in adults.
XIFAXAN® (rifaximin) 550 mg tablets are indicated for the reduction in risk of overt hepatic encephalopathy (HE) recurrence in adults.
XIF.0181.USA.23V4.0